Motivation
As the automotive industry transitions towards a more connected and autonomous future, the need for enhanced security becomes increasingly crucial. Automotive Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) have emerged as a critical component in this endeavor, providing a secure enclave for storing and managing sensitive data, cryptographic keys, and credentials. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of automotive HSMs, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and applications in the modern automotive landscape.
The rapid advancements in automotive technology have brought about a paradigm shift in the way vehicles operate. The integration of cutting-edge features like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), autonomous driving capabilities, and over-the-air (OTA) updates has transformed vehicles into sophisticated data centers, generating and exchanging vast amounts of sensitive information.
This surge in data connectivity and the increasing complexity of automotive software systems have heightened the cybersecurity risks, making the need for robust security solutions imperative.
In this regard, the ECU hardware architecture must incorporate comprehensive security measures to safeguard against unauthorized access, malware attacks, and counterfeit upgrades, ensuring the highest level of protection and data integrity. Data encryption serves as a crucial tool in safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data within the vehicle’s internal communication bus, effectively shielding it from cyber threats.
Industry Initiatives
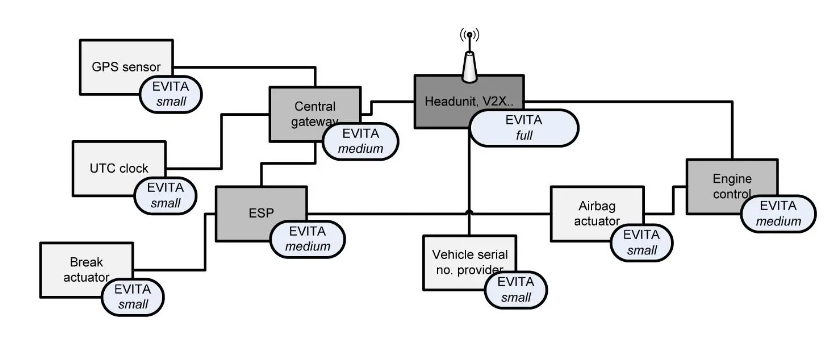
In recent years, industry initiatives have emerged to establish comprehensive system design and verification guidelines for thwarting cyberattacks and manipulations. A notable example is the EU-funded EVITA research project, involving prominent companies such as BMW, Continental, Fujitsu, Infineon, and Bosch.
The EVITA project outlines a set of guiding principles for the design, verification, and prototyping of various automotive ECU security architectures. Furthermore, EVITA mandates that all critical ECUs be equipped with chips incorporating both a dedicated hardware security module (HSM) and a CPU. Three distinct configurations are defined for HSMs: Full, Medium, and Light. These modules are responsible for encrypting and decrypting all information exchanged between ECUs.
So, what is a HSM?
Sure, here is a more professional and technically accurate rewording of the text:
“A Hardware Security Module (HSM) is a specialized peripheral device integrated into a microcontroller unit (MCU) specifically designed to implement cryptographic encryption and decryption algorithms. It typically features an independent CPU dedicated solely to encryption and decryption operations, along with dedicated hardware accelerators for specific algorithms such as AES-128, SHA-256, and others. The HSM module offloads encryption and decryption tasks from the MCU’s main CPU, allowing it to focus on other processing tasks. The HSM can either operate autonomously, returning results after a specified time interval, or interrupt the main CPU when the cryptographic operation is complete.
Furthermore, the HSM typically includes its own separate storage area, comprising RAM and NVM (Non-Volatile Memory). Under normal operating conditions, only the HSM core has access to this storage area, preventing unauthorized access by the main CPU. This isolation mechanism enhances security by safeguarding sensitive data, such as cryptographic keys, from potential exposure to the main system.
Additionally, the HSM module often incorporates common cryptographic peripherals, such as true random number generators, which are essential for generating secure cryptographic keys.”
Key applications of automotive HSM
- Protecting vehicle identity and access control: HSMs store and manage cryptographic keys used to authenticate vehicle identities and authorize access to vehicle systems. This prevents unauthorized access and ensures that only authorized users can control the vehicle’s functions.
- Secure ECU communication: HSMs facilitate secure communication between different ECUs (Electronic Control Units) within the vehicle. They encrypt and decrypt data exchanged between ECUs, preventing unauthorized interception or tampering with sensitive information.
- Digital signature generation and verification: HSMs generate digital signatures for software updates and critical data exchanged between the vehicle and external systems. This ensures the integrity and authenticity of software updates and prevents malicious software from being installed.
- Secure vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication: HSMs protect sensitive data exchanged between vehicles and other objects on the road (V2X communication). They encrypt and decrypt V2X data, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring the integrity of information used for cooperative driving applications.
- In-vehicle infotainment (IVI) security: HSMs protect personal data and copyrighted content stored in IVI systems. They encrypt and decrypt user data, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Secure key management and storage: HSMs provide a secure environment for storing and managing cryptographic keys used for various vehicle security functions. This prevents unauthorized access to keys and ensures their integrity throughout their lifecycle.
- Secure over-the-air (OTA) updates: HSMs facilitate secure OTA updates for vehicle software and firmware. They verify the authenticity and integrity of OTA updates before installation, preventing malicious updates from compromising vehicle security.
- Secure diagnostics and troubleshooting: HSMs protect sensitive diagnostic data and prevent unauthorized access to diagnostic tools. This ensures the integrity of diagnostic information and prevents unauthorized tampering with vehicle systems.
- Secure data logging and recording: HSMs protect sensitive data logs and prevent unauthorized access to vehicle logs. This ensures the integrity of data used for incident investigation and regulatory compliance.
- Secure remote vehicle access and control: HSMs facilitate secure remote access and control of vehicle functions. They verify the authenticity of remote access requests and encrypt data exchanged during remote operations.
These applications demonstrate the critical role of automotive HSMs in safeguarding modern vehicles against cyberattacks, protecting sensitive data, and ensuring the overall safety and security of passengers. As vehicles become increasingly connected and autonomous, automotive HSMs will play an even more pivotal role in preserving the integrity and security of vehicle systems and data.


