The automotive industry is experiencing a transformative era, with the rise of autonomous vehicles promising safer, more convenient, and efficient transportation. The key to understanding these innovations lies in the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) Levels of Driving Automation, a standardized system that categorizes the extent of automation in vehicles. In this blog, we delve deeper into these levels to provide a more comprehensive understanding of their significance and impact on the future of transportation.
Level 0: No Automation
Level 0 represents the baseline of the SAE scale, indicating vehicles with no automation. In this scenario, the human driver assumes full responsibility for all aspects of driving, including steering, acceleration, braking, and monitoring the environment. There are no automated assistance or safety features present, making Level 0 vehicles completely reliant on the driver’s skills and attention.
Level 1: Driver Assistance
At Level 1, the first level of automation comes into play with the introduction of driver assistance features. These features can assist with either steering or acceleration/deceleration, but not both simultaneously. For example, adaptive cruise control allows the vehicle to adjust its speed to maintain a safe following distance, while lane-keeping assistance helps the driver stay within their lane. However, it is essential to note that even at this level, the human driver is expected to be actively engaged and monitor the driving environment.
Level 2: Partial Automation
Level 2 represents a significant advancement in automation technology. In this tier, the vehicle can assist with both steering and acceleration/deceleration simultaneously, making driving more comfortable and convenient. Level 2 automation typically includes features such as lane centering and traffic jam assist, which can control the vehicle’s speed and steering in specific situations. Despite these advancements, the human driver is still responsible for monitoring the driving environment and being prepared to take control if needed.
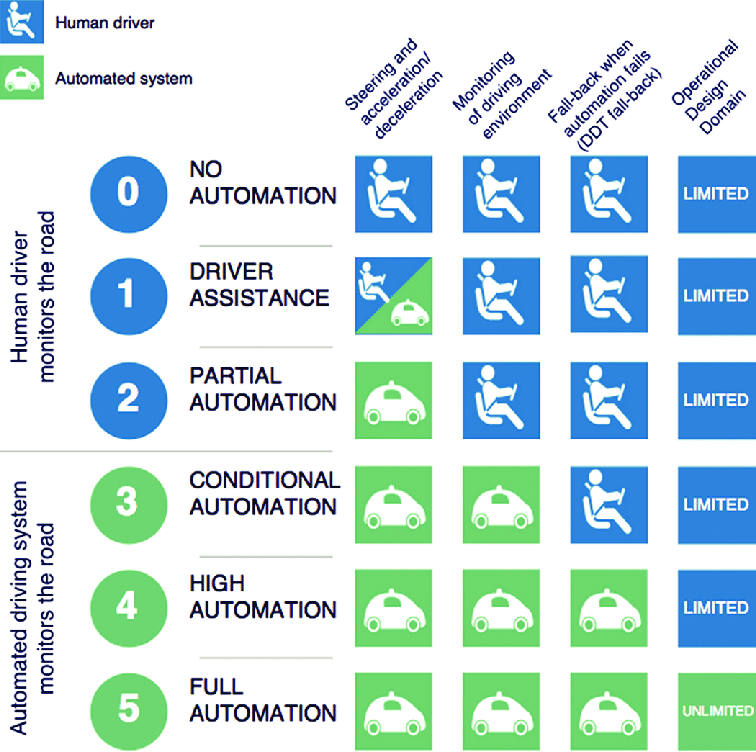
Level 3: Conditional Automation
Level 3 marks a turning point in autonomous driving technology. Vehicles at this level can handle driving tasks independently in specific conditions, such as highway driving. Advanced sensors, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras, provide a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings. The onboard computer processes this data to make real-time decisions. While the vehicle can navigate complex traffic scenarios without driver intervention, the driver must be ready to take control when the system requests assistance.
Level 4: High Automation
Level 4 takes autonomy to the next level. At this stage, vehicles are capable of full automation within predefined operational design domains (ODD). The human driver is not required to monitor the driving environment continuously, nor do they need to be ready to take control at any moment. Level 4 automation is suitable for specific, well-mapped environments, such as geo-fenced urban areas or dedicated highway segments. While this represents a significant leap towards fully autonomous transportation, it is still constrained to specific conditions.
Level 5: Full Automation
Level 5 represents the pinnacle of autonomous driving. These vehicles are entirely self-driving and capable of operating in any environment without human intervention. Level 5 vehicles rely on a combination of advanced sensors, machine learning algorithms, and high-definition mapping to navigate complex and dynamic driving scenarios. They can handle diverse weather conditions, heavy traffic, and unpredictable situations, making human drivers entirely optional.

The SAE Levels of Driving Automation offer a detailed and technical roadmap for understanding the evolution of autonomous vehicles. As technology continues to progress, we can expect further refinements in these levels, bringing us closer to a future where self-driving cars redefine the way we perceive and experience transportation. With each advancement, we move one step closer to a safer, more efficient, and convenient transportation ecosystem, shaping the future of mobility for generations to come.
